Coxarthrosis is a change in the hip joint, common among diseases, the basis of which is degenerative-dystrophic processes. The hip joint is formed by the articulation of the head of the femur with the bones of the pelvis.
This disease has a primary and a secondary form. The etiology of primary is not entirely clear, but secondary can cause a number of factors. These are trauma, inflammation, Peters pathology, necrosis of the femoral head, hip dislocation and dysplastic processes.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint causes a change in the composition and properties of the intra-articular fluid. There is an increase in the degree of its viscosity, which leads to damage to the articular surfaces. The cartilage becomes thinner, the distance between the bones that form the joint is reduced. The pressure on their surfaces increases, the deformation process is provoked.
Periodically, such a chronic condition passes into a phase of exacerbation. During this period, there is a strong pain syndrome. Outside of exacerbation, therapeutic exercises are a good preventive measure.
Etiology
There are a number of reasons why coxarthrosis of the hip joint develops. These include:
- violation of the process of blood supply to the joint - a decrease in the degree of outflow of venous blood and inflow of arterial blood. Due to the violation of trophism, metabolic products accumulate that contribute to the destruction of cartilage tissue;
- such a mechanical effect that causes an increased load on the joint;
- violations of biochemical homeostasis, hormonal imbalance;
- traumatization;
- infectious inflammation;
- state of necrosis of the femoral head;
- dysplastic disorders of cartilage and bone tissue;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- genetic predisposition;
- Congenital dislocation of the hip.
Symptoms
When a patient is contacted, the doctor conducts a survey and examination to determine the severity of the pathology.
This disease has the following symptoms: pain in the joint itself, as well as pain in the thigh, groin and knee. Impaired ability to move the affected limb. "Shortening" of the leg, as well as atrophic processes of the thigh muscles.
The nature of the pain and its strength and location depend on the stage. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies. Due to emerging muscle atrophy, knee pain occurs. For this reason, sometimes there is an error in the diagnosis - they suggest arthrosis of the knee joint. It is necessary to contact experienced specialists who will be able to make a differential diagnosis and schedule the necessary appointments. Only a doctor can determine the disease and find out what kind of therapy the patient needs.
Degrees
The following degrees of the disease are distinguished.
- First grade. This degree is characterized by pain syndrome, provoked by stress. Localization of pain: the hip joint, less often - the thigh and knee. On the x-ray, small growths of bone tissue are visible.
- Second grade. At this degree of the disease, the pain intensifies, its intensity increases. Localization extends to the thigh and groin area. The pain also occurs at rest. Movements are limited, and radiographs reveal volumetric growths of bone tissue. Cysts sometimes form in places of increased stress.
- Third degree. This grade is characterized by constant pain. Walking is difficult. Severe atrophy of the muscles of the thigh, buttocks and lower leg. The limb is markedly shortened. X-rays show extensive growths of bone tissue.
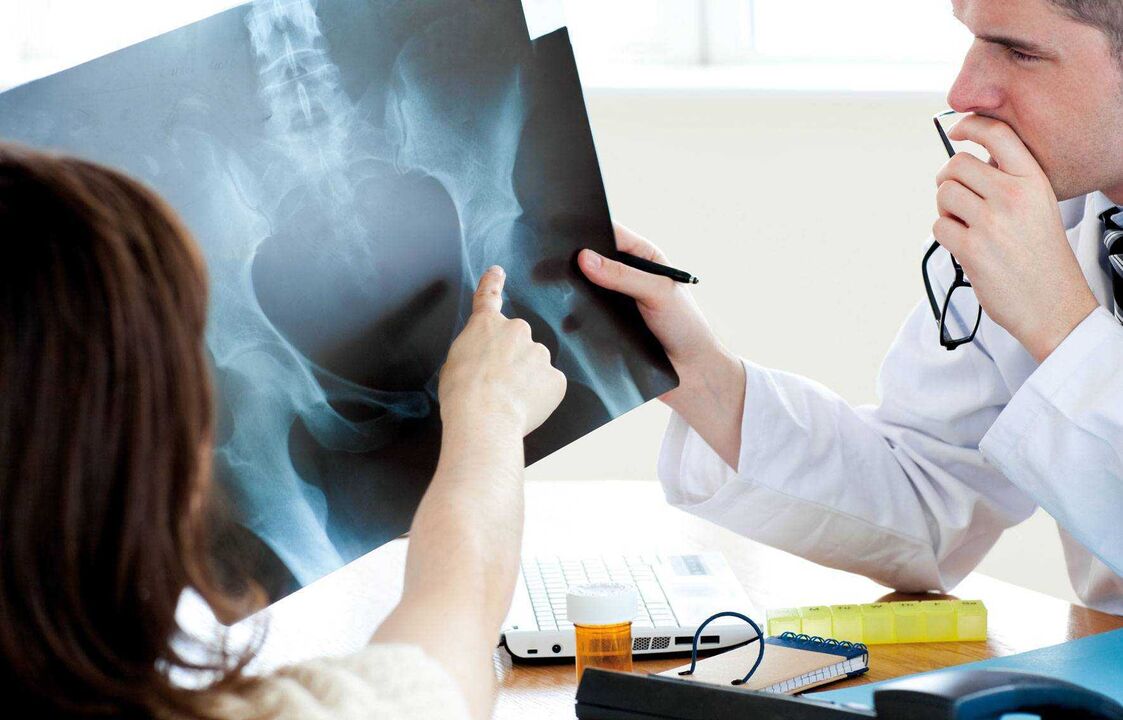
Diagnosis
The main diagnostic method is X-ray examination. With its help, the doctor can determine the etiology and stage of development of the disease, determine the need for surgery. For example, with dysplasia, the doctor will notice the bevel and thickening of the acetabulum. An x-ray of coxarthrosis resulting from injury makes it possible to see the shape of the articular bones after their restoration. Coxarthrosis, which developed as a result of necrosis of the femoral head, also has a characteristic X-ray image.
Therapy
The question of how to treat coxarthrosis of the hip joint can only be answered by a doctor. The nature of treatment varies depending on the degree of localization of the disease, as well as the intensity of pain. It is dangerous to self-medicate at home. With coxarthrosis of the third degree, it is possible to cure the disease only with the help of arthroplasty, in which the doctor replaces the joint by installing an artificial prosthesis. Surgery is often necessary for coxarthrosis, which arises due to necrosis of the femoral head.
In the treatment of pathology of the first and second degree, surgery is not required. Medical and physiotherapeutic treatment is used, which is prescribed by the attending physician, as well as therapeutic exercises, which can be used at home.

medical therapy
Drug treatment includes medications such as tablets, injections, and ointments.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They can relieve pain, stop inflammation and swelling, and the downside is a decrease in the regenerative capacity of cartilage. If they are not effective, the drugs are replaced. The dosage form of some drugs - injections - is the most effective.
- Vasodilator drugs. The action is aimed at relaxing muscle tissue and expanding the lumen of blood vessels. Improves blood supply.
- Muscle relaxants (medicines for muscle relaxation). They relieve muscle spasms and improve blood circulation.
- Chondroprotective drugs. Contribute to the restoration of cartilage tissue. Regular use allows you to completely stop the development of the disease.
- Hormone therapy. High-quality injections containing these substances help relieve inflammation. It is necessary to take a break of a week between injections.
- Local preparations - ointments, compresses. These drugs improve blood circulation and help eliminate pain caused by muscle spasm.
With the help of the complex of the listed drugs, the disease can be cured.
Physiotherapy
It includes a number of procedures, namely electrotherapy, inductothermy, magnetotherapy and ultrasound therapy. UHF therapy, laser therapy, phototherapy and aeroionotherapy.
All of these techniques are applicable to improve blood supply to the joint and help relieve muscle spasm. Procedures are performed by a physician specializing in physical therapy.
Massage
Massage is an effective way to treat this pathology: it improves blood circulation, strengthens muscles, relieves spastic pain, swelling. With its help, the distance between the articular surfaces increases. Massage can be done at home, but only after the recommendations of a specialist.

joint traction
Produced manually or using pulling devices. It leads to a decrease in the load on the joint and an increase in the distance between the joint surfaces. This procedure is performed only by a doctor with a high level of qualification. It cannot be done at home.
Diet
Required if necessary to reduce body weight. This helps reduce stress on the joint.
Gym
A good effect in coxarthrosis has therapeutic exercises. The doctor selects special exercises to strengthen the muscles, so that they do not increase the load on the joint area. Proper therapeutic exercises can alleviate the condition, strengthen the muscles. It can be done at home. In addition, swimming is very useful.
Alternative treatment is also used in the treatment of coxarthrosis, but all its methods must be agreed with the attending physician.
It should be noted that the treatment of coxarthrosis must be complex. Physiotherapy and massage should not be neglected. You also need to do the exercises recommended by Therapeutic Exercises. You can not self-medicate, so as not to harm your health. Any medication should be prescribed only by a doctor. Proper treatment will help eliminate the need for surgery.















































